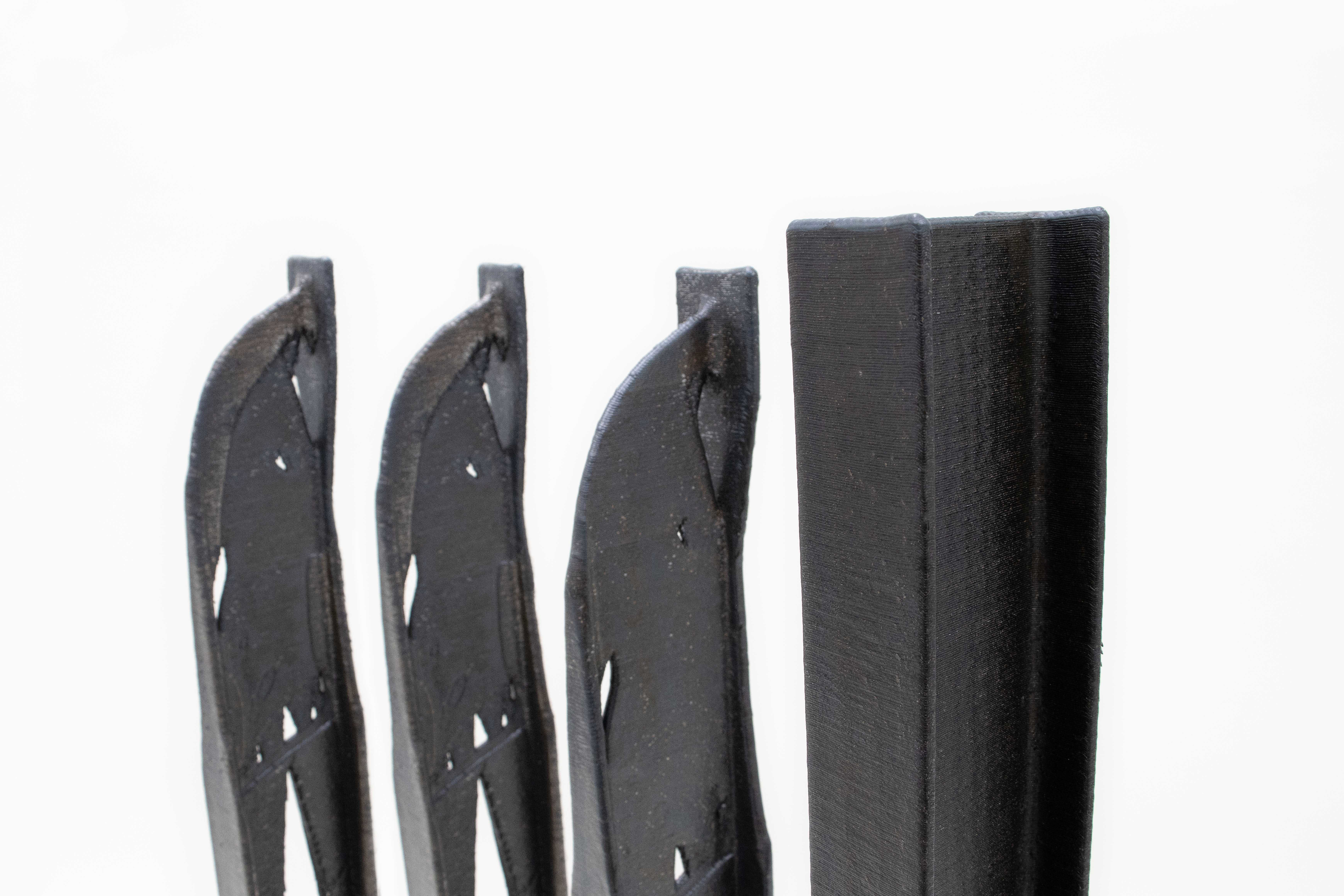
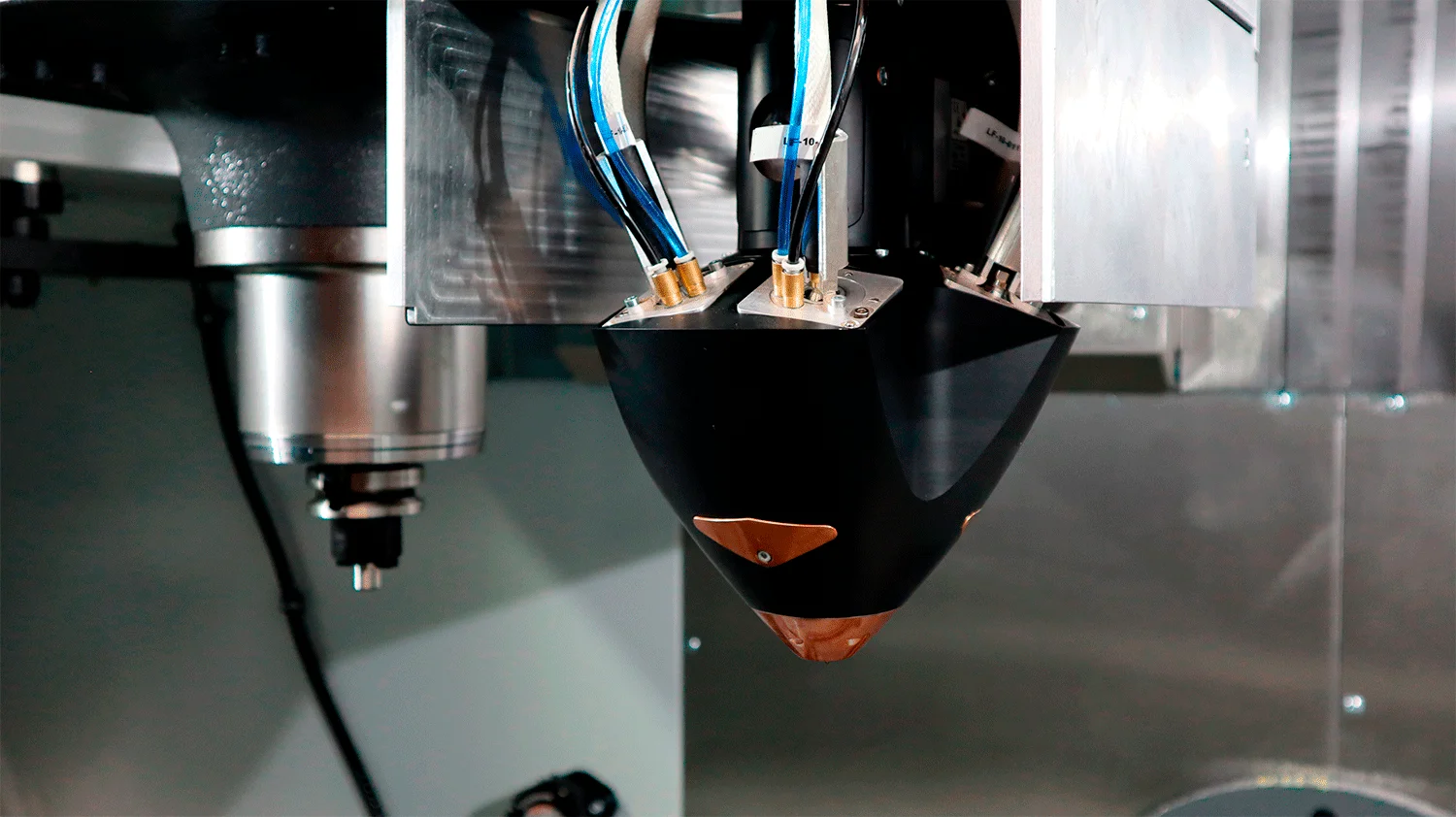
There are several industrial possibilities within additive technology that can change the future and bring the industrial world into a new era. In this blog post, you will find some of the most important features of metal 3D printing which constitutes the strength of “metal additive manufacturing”.
The advantages won’t be fulfilled, but you will have a better understanding of how you can use the power of technology and how it can change production and the approach to it.
Always the same: Prototyping – simpler, faster, cheaper – but now also a little more
The above sentence is probably the established image of additive technology. Every time we talk about additive processes and additive technology, we mention how excellent it is in prototyping processes and R&D departments. It speeds up decision-making, increases the creativity of creators, reduces costs, and shortens the time a new product enters the market.
However, metal 3D printing technology takes it to a much higher level and makes the process even easier. Like no other commonly known technology, it gives us:
- Possibility of using the final material and functional prototyping: Many times we encounter companies interest in incremental processes in terms of the initial design of new elements. Now, metal 3D printing makes it possible to produce functional elements that can be tested and checked in final operation conditions. This is a great change in work methodology and risk minimization – which is a key element of a safe R&D process.
- Possibility to improve the design at any time: You need to add a unique point here, unique to metal printing, i.e. a change to the idea that can be introduced without having to re-print the entire element. Not all metal 3D printing technologies offer this possibility, but many of them enable the addition of elements to existing elements. This significantly speeds up processes and, as above, makes creation processes safer and cheaper.
- Access to increased personalization of solutions: This involves the possibility of mixing the product raw material, both during work (mixing powders and, in simple terms, creating your own alloys) and also by replacing the material during the process, which allows for even greater “personalization” of the properties of the printed element. For the designer, it is like opening another door to “making” the application more efficient, and more secure – just as it should be.
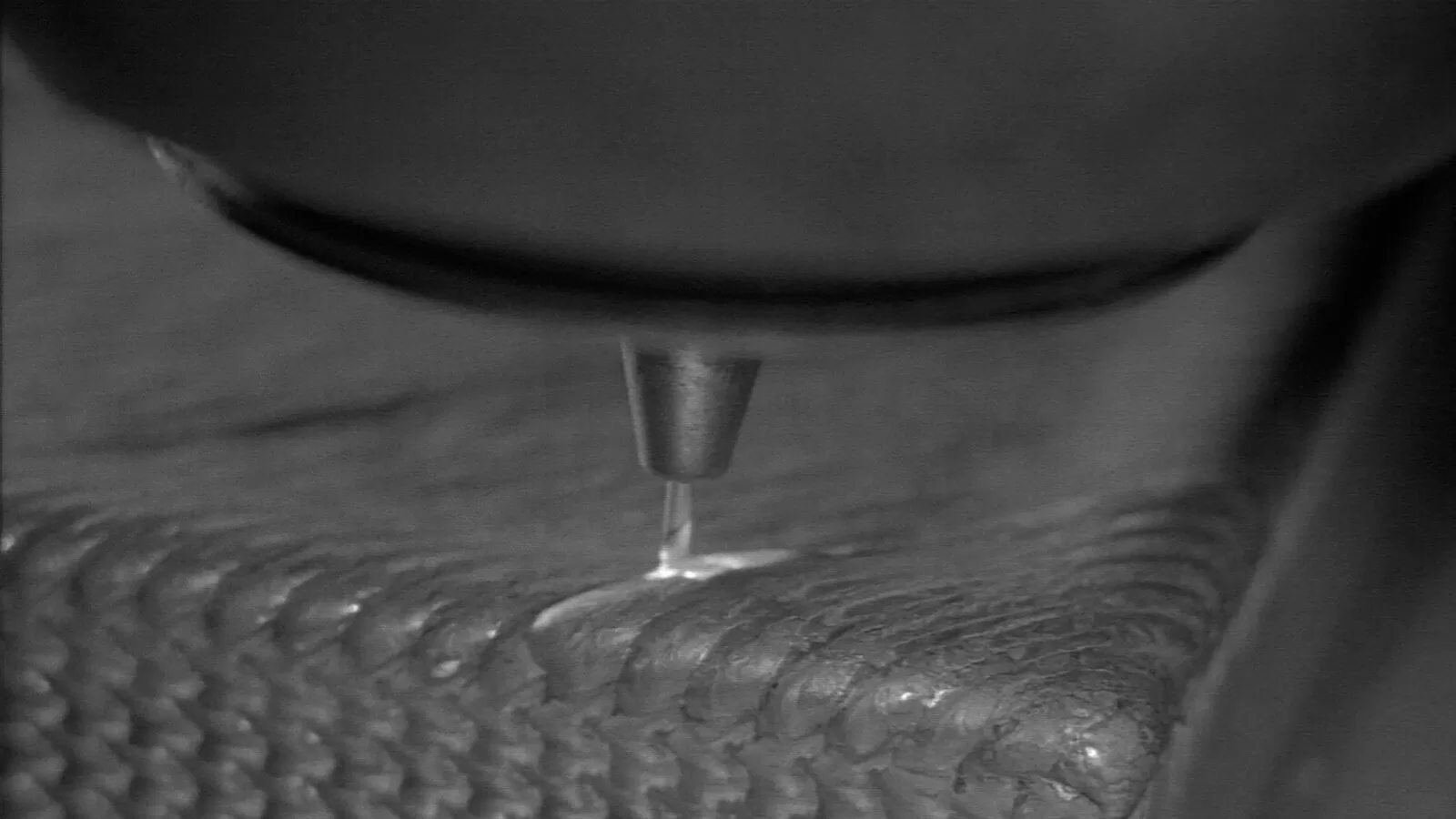

Metal 3D printing proves mass production can be done
The features listed above can also be used effectively in mass production. However one of the main advantages of metal additive technology is the efficiency of the process and the range of efficiencies available. There are technologies that can produce a few grams per hour, but there are also devices that print over 30 kg per hour.
This, combined with the possibility of using various raw material variants, building elements from scratch taking into account the internal structure, shortening the production time, and greater freedom of “personalization” of solutions, is a milestone in the future approach to production. Additional advantages are:
- Minimization of personnel service: as we are dealing with the standardization of raw materials and high standardization of production equipment (generally no additional production tools), we minimize the need for the presence of service personnel. In extreme cases, production can be performed remotely – even over long distances.
- 3D printing as part of the process: one of the key elements of metal 3D printing is that the printed elements can be freely processed in currently used devices. As we print from metal, any mechanical and aggressive chemical post-processing that is and has been used in the current process may remain unchanged. This further demonstrates the genius of this variant of additive technology, which is simple to implement in current processes.
- Hybrid solutions: some devices using metal 3D printing are also characterized by the possibility of integration with currently operating devices (CNC machines or robots) in production processes. This feature additionally expands the capabilities of currently used processes – creating hybrid solutions. For example, a combination of additive and reduction technologies in one CNC device. It can significantly change production – making the process optimal in every respect.
TIP: If you want to deep dive into metal 3D printing, read the article about The benefits of a Wire-based Metal 3D Printing process.
Greater durability: “structural” optimization of the product and the production process
It has always been said that one of the main features of 3D printing was the ability to optimize printed elements in terms of weight and strength. In this respect, 3D metal printing goes further again. A significant part of the technologies used in the world of additive metal create elements with greater mechanical strength than those traditionally obtained in the forging or casting process.
This is mainly due to the process being “concentrated” into a specific small point or area, allowing for better control. Like few additive technologies – metal 3D printing – can optimize manufactured elements in terms of isotropic properties. All these features make it possible to optimize the print in almost every respect regarding durability, giving producers:
- Possibility to reduce the operational “stress”: Of a given element and extend its service life through the ability to determine and produce the internal structure, but also greater geometric freedom – 3D metal prints can minimize the loads that arise during the use of the product.
- Design optimization: Thanks to the use of the above-mentioned material variability – which can not only affect the properties of the element but also reduce the cost of its production.
- Significant improvement of tool capabilities: Thanks to the fact that we can approach the construction of elements differently, we can also change the tools needed for production. Using 3D printing, we can, among others: change the “thinking” about the production of molds which, using metal additive manufacturing, can be equipped with, for example, cooling channels, or which we can “repair” or rebuild as part of a changing project. Using the feature described in the section on prototyping, i.e. the freedom to add elements to existing parts.
“0 Waste” approach: A new dimension of modern production, a new dimension of savings
When creating a modern production system, the most important point is often the maximum reduction of costs. 3D printing itself saves materials, being the only methodology that creates elements from scratch. Possible waste mainly results from the need to use supports or post-processing. This is the next and last “most important” benefit of metal 3D printing.
Whether it is the above-mentioned hybrid applications or printed elements themselves – if they require post-processing, in much of the additive metal world there is little or no post-processing. A real alternative to full reduction processing, which can complete this process – by not filling the element internally and at the same time limit the external processing to a minimum or nothing, because the printout is close to the net dimensions of our element.
No other technology fits into “0 Waste” like metal printing, and what’s more, its implementation does not mean a change in production; we just need to assume that we are enriching it with new possibilities – in line with the spirit of waste reduction and process optimization.
We will find a few more important features of metal 3D printing that have not been listed here. They often reflect the entire world of 3D printing. After all, 3D metal printing is only a fragment of an increasingly large area of industrial activity.
The above benefits do not exhaust the topic – but they are the elements that can have the greatest impact on the realities of industrial production… and in a very short time.
TIP: If you want to know more about metal 3D printing and how it can help and improve your manufacturing capabilities, watch this insightful webinar about Dual Wire Metal 3D Printing.