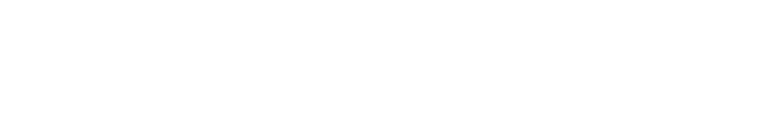Within the domain of 3D metal printing, specifically in Wire-Laser Directed Energy Deposition (DED), the concept of process control plays a critical role in ensuring optimal printing results.
The primary goal is to maintain a delicate energy balance between the substrate and wire, essential for achieving accurate printed objects. This equilibrium, influenced by the distance between the nozzle and substrate, is where the process control comes into play.
Meltio introduces an innovative process control mechanism that proactively adjusts feed rates, effectively managing melt pool continuity disruptions through dynamic feed speed adjustments. This ongoing oversight significantly aids in anticipating common printing imperfections, thus ensuring flawless printed outcomes.
Ideal Printing Process
To ensure a stable process, maintaining energy balance between the base material (substrate) and the wire is crucial. Deviations from this balance can lead to process failure, like dripping from excess energy or substrate-absorbed energy causing stubbing.
Given the fixed laser angle, this energy balance is primarily influenced by the nozzle-substrate distance (working distance). When this distance becomes excessively large, the energy is directed towards the wire, risking undesired dripping. Conversely, if this distance becomes too small, the energy dissipates within the substrate, leading to energy loss.
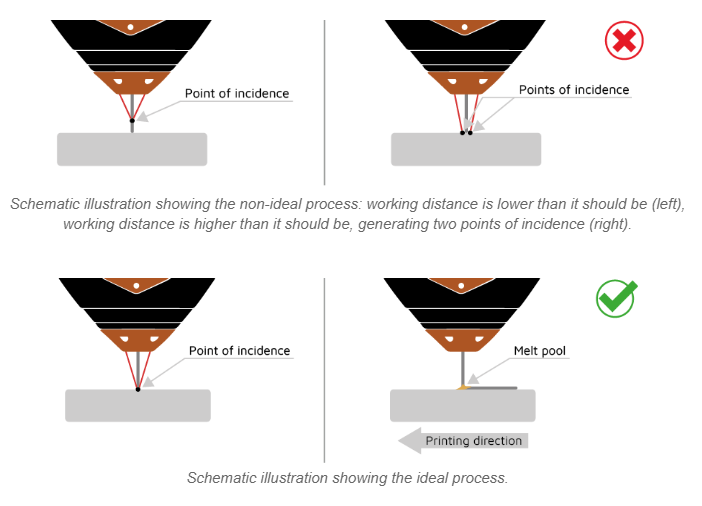
The process involves three steps:
- Extrusion: The wire extends until it contacts the build plate, activating lasers upon pressure detection.
- Deposition: The lasers are heated to the designated power level, and the wire extrudes at a specific speed while the printing is moving through the axes.
- Retraction: The lasers turn off and the wire retracts. An axis movement is performed without extruding any wire. The process then recommences with the extrusion step.
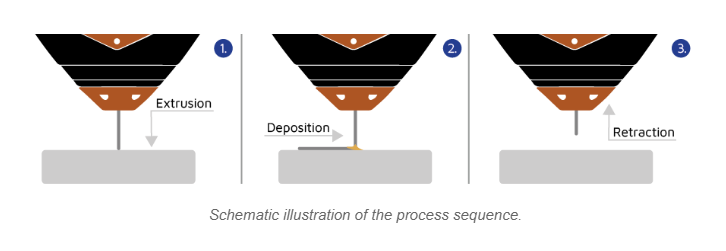
Process Control
At the core of Meltio’s innovation lies its process control approach. This system involves constant real-time monitoring of electrical continuity between the bed (V-) and the head (V+) during the print deposition process. By continuously monitoring the continuity, it can identify any deposition deficiency in the part being printed as it has instantaneous visibility into its continuity throughout the entire printing process.
The system’s ability to detect interruptions in melt pool continuity serves as a pivotal indicator of material insufficiency, subsequently triggering swift adjustments in feed speed to ensure precise refilling.
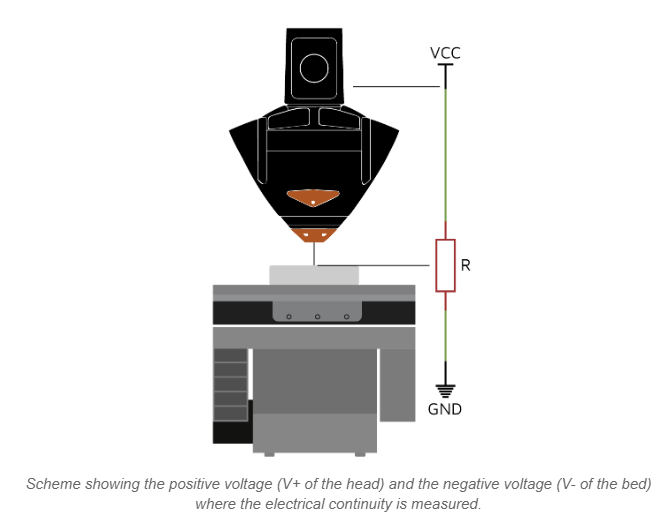
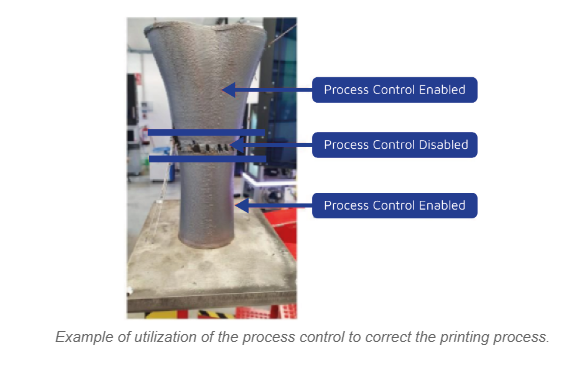
When process control is disabled and deposition calculations are not accurate, there is a significant probability of generating printing issues such as dripping defects or incomplete material deposition, resulting in holes, porosity, and other similar inconsistencies. However, with a properly configured process control, the Meltio system promptly detects and rectifies any errors in the subsequent layer, ensuring precise and defect-free printing.
2.1. Closed Loop Control Algorithm
The closed loop control algorithm incorporates a continuous feedback mechanism that constantly updates the controller with information regarding the continuity between the deposition head and the printing bed. Based on this real-time data, the controller is able to make adjustments to the feeder speed or laser power as necessary.
When disruptions are detected, a controller swiftly assumes control over the printing power and deposition speed of the feeder drive wheel. This allows for a rapid increase in the material added to the specific area where the discontinuity was detected, all within a matter of milliseconds. Once electrical continuity is restored, the deposition process resumes seamlessly.

Conclusion
Unlike conventional metal 3D printing systems, Meltio’s innovative approach embraces the use of welding wire in tandem with an advanced coaxial deposition head housing six surrounding lasers. This synergy naturally imbues the process with a high degree of control.
Any deviations from the ideal process are promptly compensated through meticulously tested sensors and readings within Meltio’s R&D framework, eliminating the need for customers to incorporate additional devices, technical expertise, or elaborate monitoring setups.
Furthermore, the process control system assumes a central role in proactively addressing the most prevalent defects in wire-laser DED 3D printing. This forward-looking intervention targets issues such as dripping, balling, overbuilding, necking, and stubbing, thereby ensuring a smoother and more confident printing journey.