Agile metal production
by replacing molds and casts
Case study developed by Daidore
Agile metal production
by replacing molds and casts
Case study developed by Daidore
Daidore Corporation is a Japanese manufacturing company with a focus on agile product development and efficient production of industrial components. The company has increasingly positioned itself as an early adopter of innovative manufacturing solutions to stay ahead in a competitive and rapidly evolving industrial landscape.
Faced with mounting pressure to streamline production and shorten development cycles, Daidore began evaluating advanced manufacturing technologies that could improve both productivity and product quality.
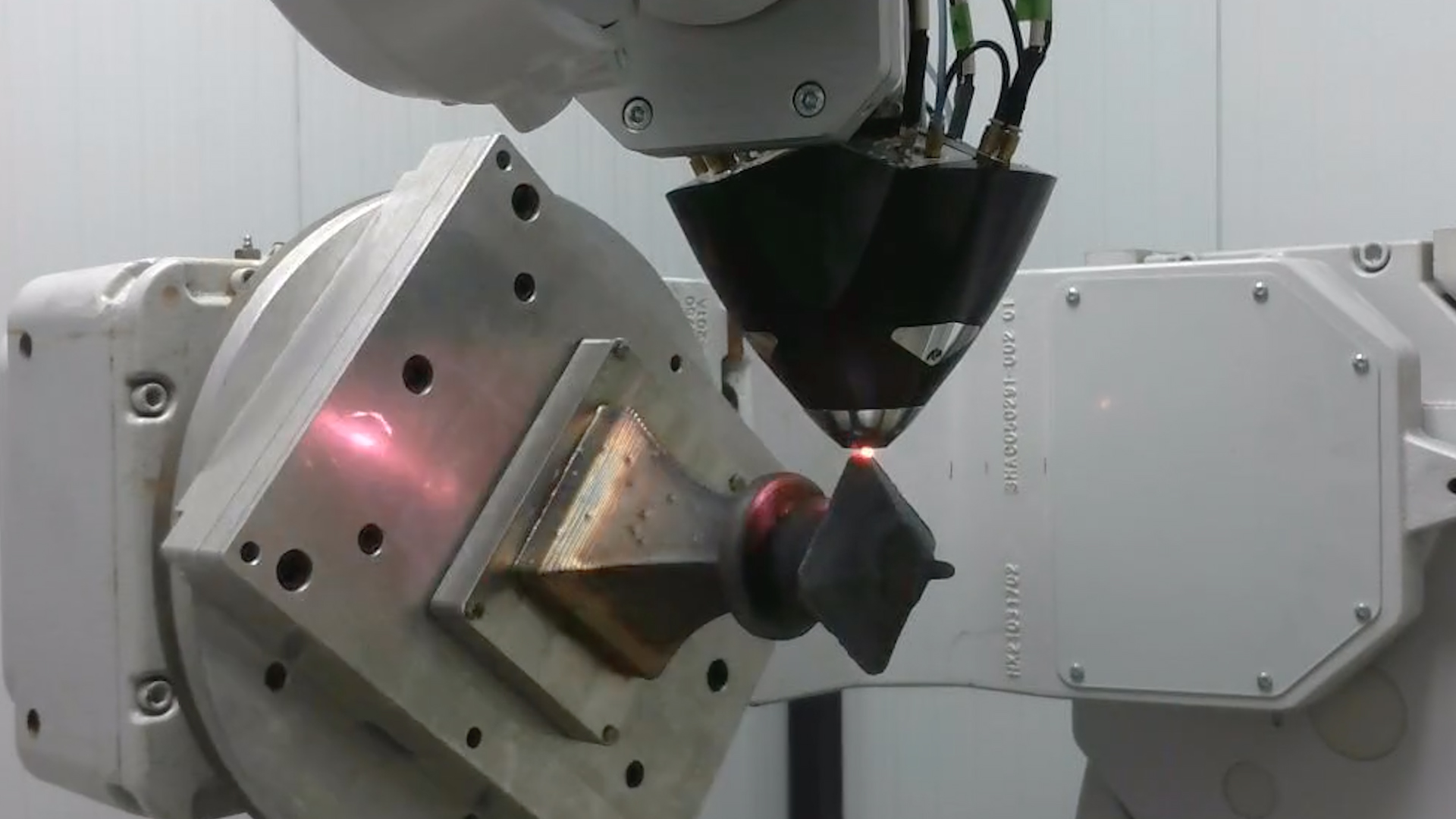
Strategic initiative to reduce costs and accelerate product development
The company’s traditional manufacturing processes—particularly when relying on cast parts or producing components without existing molds or design drawings—were proving too slow and expensive for today’s fast-paced industrial demands.
Additionally, Daidore needed a way to:
Accelerate its new product development timelines
Eliminate the dependency on expensive tooling and casting processes
Improve flexibility in responding to low-volume and custom orders
Reduce the cost and lead time associated with part procurement
Recognizing that additive manufacturing (AM) could address these pain points, Daidore established the implementation of 3D printing as a strategic corporate initiative.
Key features driving Meltio adoption
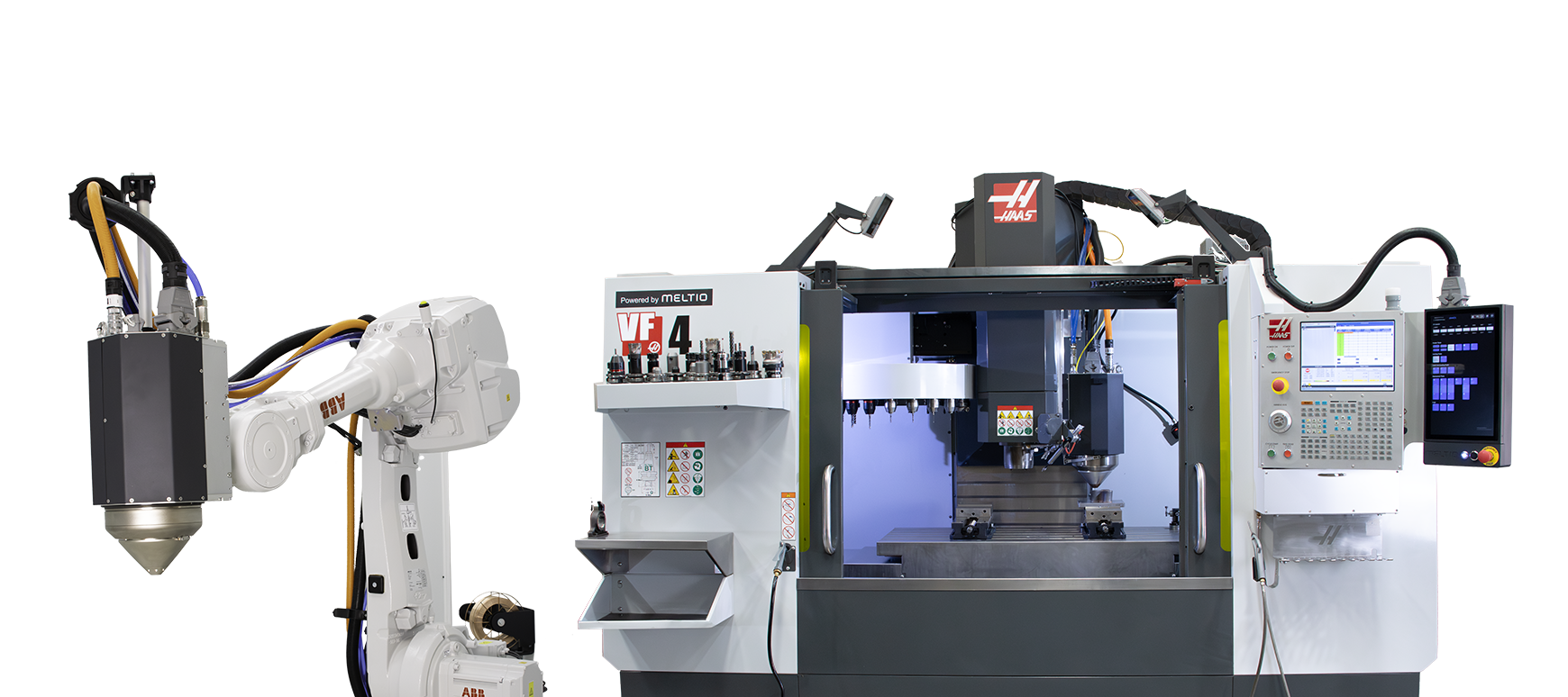
After evaluating several additive manufacturing technologies—including powder-bed fusion and binder jetting systems—Daidore selected Meltio’s wire-laser metal deposition technology, specifically the Meltio Robot Cell, due to its unique combination of affordability, flexibility, and scalability.
Key features that influenced the decision:
Material cost efficiency
Meltio’s wire-based AM uses welding wire, reducing material costs by up to 80–90% compared to powder-based systems
Advanced geometrical capability
The integration of a 6-axis robotic arm combined with a dual-axis rotating build table allows for the creation of more complex and organic geometries, while minimizing the need for support structures
Large build volume
The Meltio Robot Cell provides a build area of 2m × 1m × 1m, ideal for fabricating large parts or producing multiple components in one batch
Simplified infrastructure requirements
Unlike powder-based AM, Meltio’s system requires no explosion-proof facilities, sintering, or degreasing equipment—streamlining the implementation and reducing operational risk
Multi-material capability
Meltio enables the deposition of up to two different metal materials within the same part or job, opening new doors for functional and hybrid applications
The combination of these features provided Daidore with a cost-effective, versatile manufacturing tool that could be quickly adopted and scaled as needed.
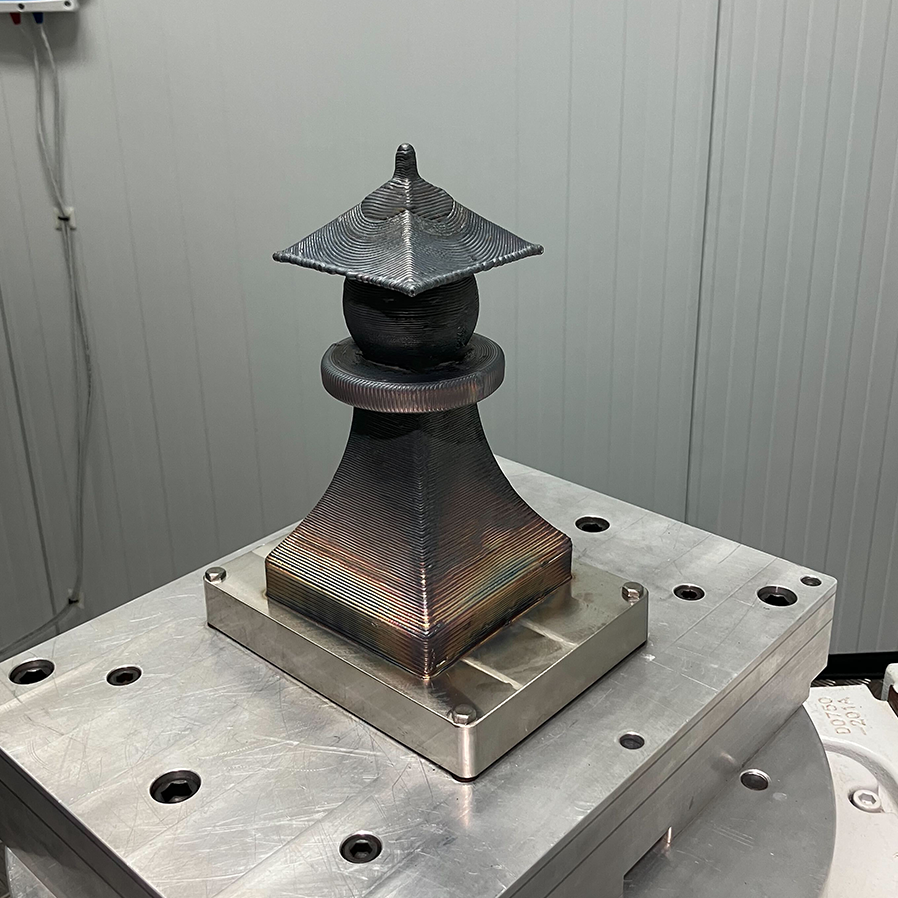

From casting replacement to custom jigs
Since implementing the Meltio Robot Cell, Daidore has applied the technology across a wide range of manufacturing activities, including:
Replacement of cast parts
Eliminating long lead times and costly tooling by directly manufacturing metal parts on demand
New product development
Producing functional prototypes rapidly to support R&D activities and reduce time to market
Tool-less part fabrication
Manufacturing metal components without the need for existing molds or drawings, using reverse engineering or design-from-scratch workflows
Tool-less part fabrication
Manufacturing metal components without the need for existing molds or drawings, using reverse engineering or design-from-scratch workflows
Discontinued product reproduction
Reviving legacy parts where tooling is unavailable or obsolete
Machining jig production
Creating custom jigs in-house to support production and quality assurance processes.
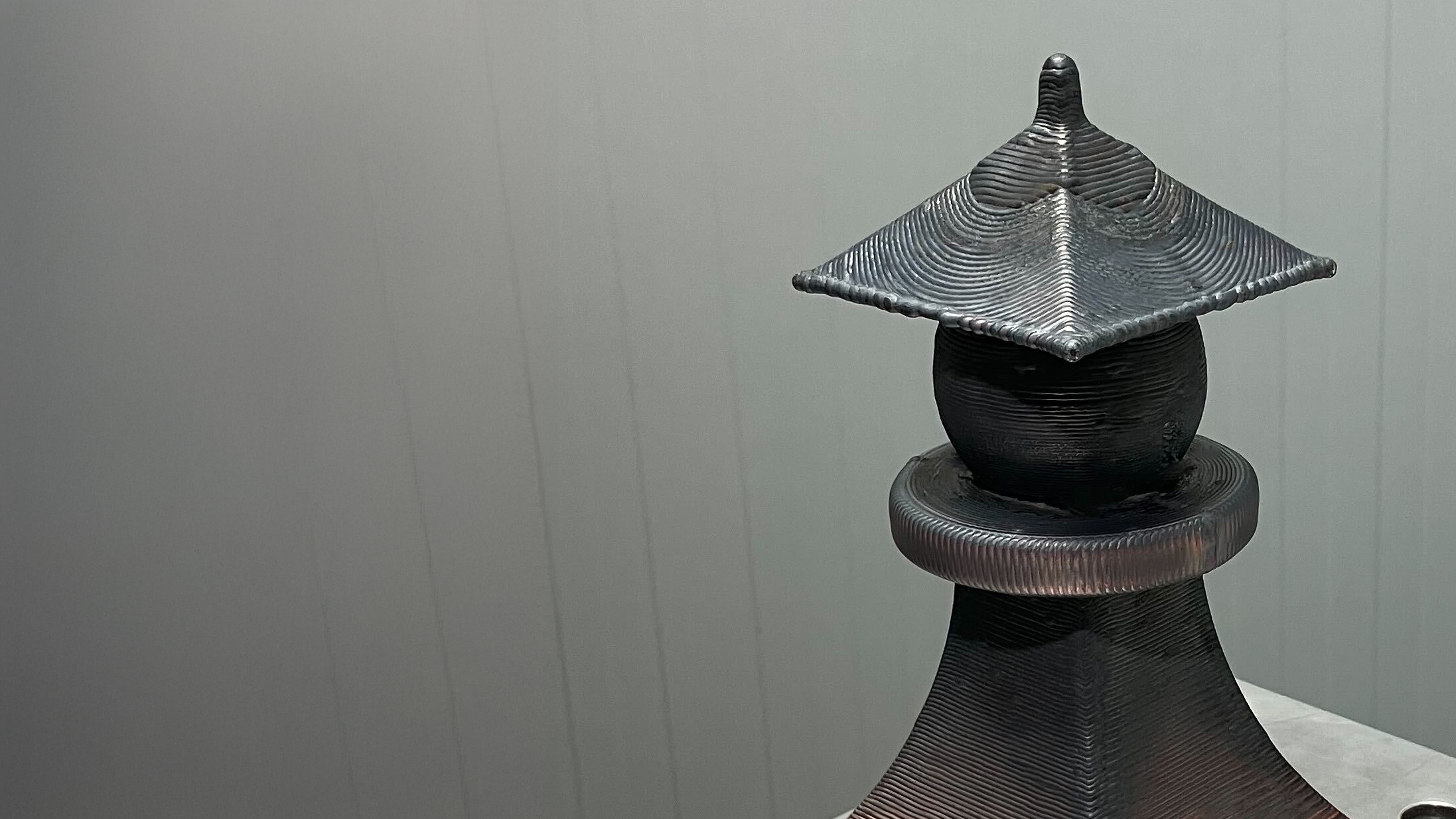

These improvements have positioned Daidore to respond more quickly to customer needs and explore new business opportunities.
Shortened production cycles
Lower operation costs
Greater design freedom
Increased production autonomy
Meltio 3D Printing Solutions
Unlock the potential of metal 3D printing with Meltio. Your journey starts here.

Meltio 3D Printing Solutions
Unlock the potential of metal 3D printing with Meltio. Your journey starts here.

System: Meltio Robot Cell
It is designed to provide industries with a secure and efficient solution for manufacturing metal 3D printed parts.
Sector: R&D & Aerospace
Meltio meets Class 1 laser safety standards, ensuring no harmful laser exposure to the operator.
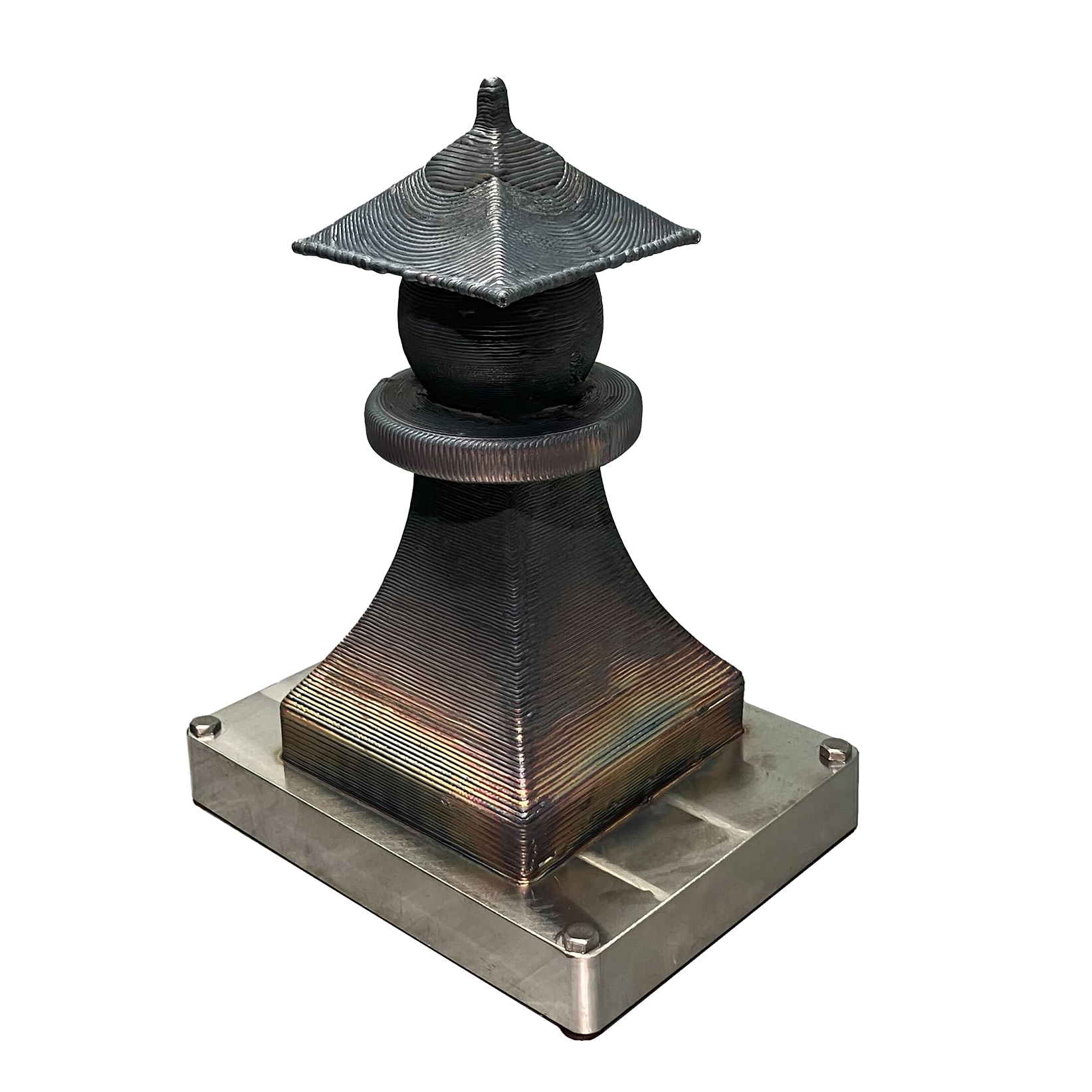
Material: Stainless Steel
Wire feedstock proves more affordable and safer than powder-based alternatives.
Printing Time: 5h 34min
Production time was 3 weeks

Additive manufacturing as a business enabler
Looking ahead, Daidore has outlined a comprehensive strategy to integrate Meltio’s technology more deeply into its operations.
The company plans to:
Scale up prototype production to support a broader range of new product development projects
Expand its use of Meltio for small-lot and custom manufacturing, particularly where traditional methods are uneconomical
Incorporate Meltio into the company’s supply chain operations to streamline order processing and reduce third-party dependencies
In the short term, Daidore’s objective is to enhance its product development capabilities and improve part quality while continuing to master Meltio’s technology.
In the long term, the company aims to use 3D printing as a platform for launching entirely new business models, improve its overall technical know-how, and build a competitive edge rooted in additive manufacturing.
Building long-term growth
Daidore Corporation’s adoption of Meltio’s wire-laser metal AM technology marks a pivotal step in its transition toward a more flexible, efficient, and future-ready manufacturing model. By leveraging the Meltio Robot Cell, the company is not only solving current production challenges but also laying the foundation for innovation, growth, and sustained competitive advantage in the years to come.
Want to know more about printed parts properties?
Want to know more about printed parts properties?